
-

生物通官微
陪你抓住生命科技
跳动的脉搏
章元明教授团队在关联分析方法学研究中取得突破性进展
【字体: 大 中 小 】 时间:2022年02月25日 来源:华中农业大学植物科学技术学院
编辑推荐:
南湖新闻网讯(通讯员 李梅 张亚雯 周亚慧)2022年2月20日,我校植物科学技术学院章元明教授团队在植物学领域期刊Molecular Plant上发表了题为“A compressed variance component mixed model for detecting QTNs, and QTN-by-environment and QTN-by-QTN interactions in genome-wide association studies”的研究论文,报道了关联分析方法学研究的突破性进展
南湖新闻网讯(通讯员 李梅 张亚雯 周亚慧)2022年2月20日,我校植物科学技术学院章元明教授团队在植物学领域期刊Molecular Plant上发表了题为“A compressed variance component mixed model for detecting QTNs, and QTN-by-environment and QTN-by-QTN interactions in genome-wide association studies”的研究论文,报道了关联分析方法学研究的突破性进展。
该研究显著减少了混合模型中方差组分的数目,统一构建了关联分析主效位点、环境互作和位点间互作检测以全面剖析数量性状遗传构成的新框架,实现了从单环境数据关联分析到多环境数据联合分析的转变,为复杂性状基因发掘提供了新方法。
全基因组关联分析是在自然群体中将标记基因型与复杂性状表型关联以挖掘复杂性状基因的方法,在动物、植物、林木和人类遗传中广泛应用。在QTN检测中,虽然关联群体标记通常有AA、Aa和aa三种基因型,应该估计加性与显性两种效应,但是目前的几乎所有方法只估计等位基因替代效应,导致效应估计混杂和多基因背景控制不全面。在QTN×环境互作(QEI)和QTN×QTN互作(QQI)检测中,除上述问题外,还存在可供利用的方法十分有限,导致了作物关联分析几乎是单环境数据分析或多环境BLUP值分析,少见QEI和QQI的应用研究报道。
在QTN检测全基因组扫描时,新提出的压缩方差组分混合模型首先估计标记基因型AA、Aa和aa的效应,然后将这些基因型效应估计值剖分为QTN的加性与显性效应。这种模型与我们已提出的mrMLM方法结合,形成3VmrMLM方法。同时,这种方法延伸至QEI和QQI检测。由此,将QTN、QEI和QQI检测的5、10和15个方差组分混合模型统一压缩为3个方差组分的混合模型,构建了一个能检测各种位点并估计其效应的统一关联分析新框架(图1)。
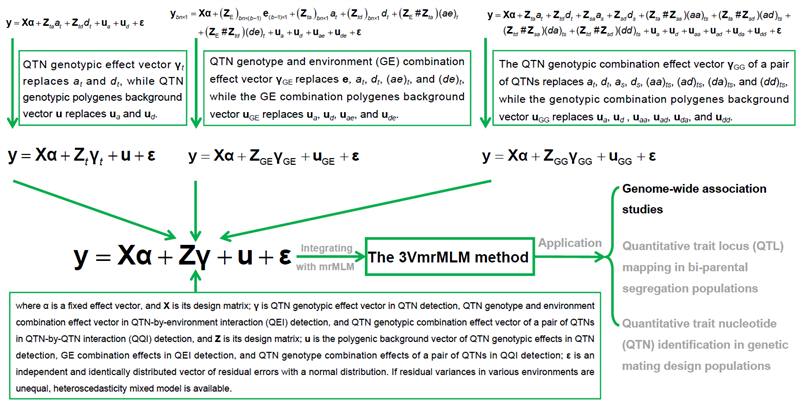
图1. 3VmrMLM方法的统一框架
在Monte Carlo模拟研究中,3VmrMLM正确检测了所有主效与互作效应位点并渐进无偏估计其效应,具有高的检测功效、高的效应与位置估计精度和低的假阳性率(图2)。
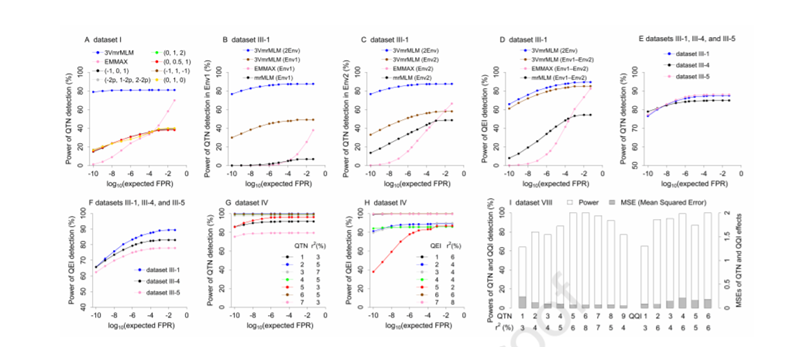
图2. 模拟研究中QTN、QEI和QQI的检测功效以及QTN和QQI效应估计的均方误差
用3VmrMLM重新分析了Huang et al. (2015)的1439个杂种F1数据集(1098527个SNP标记;10个产量和品质性状)。结果表明:在主效QTNs附近共发掘了269个已报道的与性状真正关联的基因,在QEIs附近共发掘了45个已报道的与性状真正关联的基因×环境互作,在QQIs附近共发掘了20个已报道的与性状真正关联的基因×基因互作,验证了3VmrMLM的有效性。水稻抽穗期的结果如图3所示。
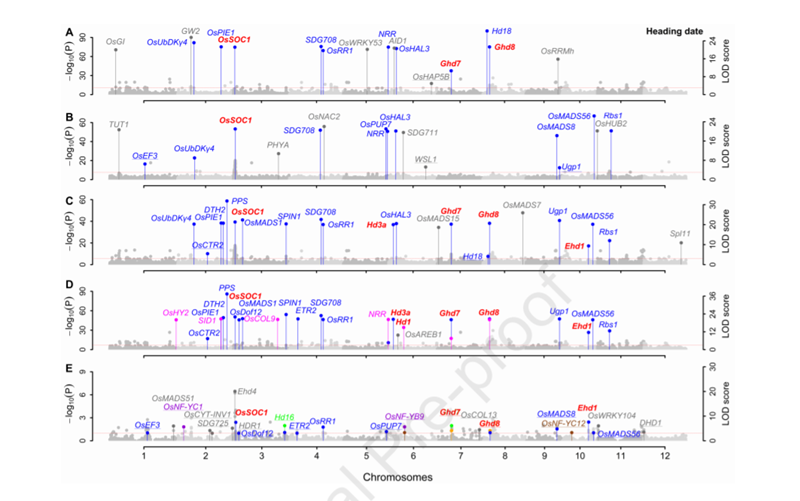
图3. 水稻抽穗期关联分析的曼哈顿图(数据来自Huang等(2015))
进一步分析所有10个性状已知基因附近的QTNs、QEIs和QQIs发现:有67.49%位点的R2≤1,35.52%的位点稀有等位基因频率≤0.10,说明3VmrMLM对小效应、稀有等位基因频率位点有较强的检测能力;有30.54%的多效基因,54.36%的基因被两个以上数据集重复检测,进一步说明了实际数据分析结果的可靠性和高的可重复性。此外,多环境数据关联分析新策略能更全面揭示复杂性状的遗传基础。
在QEI检测中,发现不同环境间检测结果不稳定的可能原因之一是同一(或连锁)位点的主效与环境互作效应的叠加。当关联群体较大时,建议采用不同试验设计及其统计分析方法来校正复杂性状表型观测值,以控制区组内误差。当环境间误差方差异质时,我们新发展的异质方差混合模型方法也是有效的。当环境数较大时,两种维数减少方法也有相似的效果。这种新方法还能在动物和人类遗传中应用。在QQI检测中,提出的具有多基因背景的变量选择方法具有较高检测功效与参数估计精度,还发现加显互作或显加互作有时会误判为主效的现象并提出了解决办法。
章元明教授领衔的统计基因组学团队多年聚焦于作物复杂性状基因发掘方法学研究,取得了一系列成果。在关联分析方面,最早提出关联分析混合模型方法,联合优化压缩混合模型方法,发展的一系列多位点方法已被广泛应用;在双亲分离群体基因发掘方面,提出了高功效检测小效应与连锁位点的GCIM方法、F2群体极端池基因快速检测的平滑LOD得分统计量以及将Bayesian估计似然化的惩罚最大似然方法,参与发展了多QTL检测的压缩Bayesian估计方法。这些结果在Mol Plant (2019, 2022)、Brief Bioinform (2018, 2019, 2022)、BMC Biol (2014)、Genom Proteom Bioinf (2020)、Plant J (2020)、J Exp Bot (2020)和Genetics (2005)等刊物上发表。
我校植物科学技术学院博士生李梅和博士后张亚雯为该论文的同等贡献第一作者,章元明教授为通讯作者,其R软件包即将在R平台上发布。最近,章元明教授团队将上述压缩方差组分混合模型与GCIM方法结合,提出了IMF2和F2:3设计固定效应与随机效应的GCIM-QEI检测新方法,提高了小效应与连锁QTL和QEI的检测功效与参数估计精度,同时降低了假阳性率。论文已在Brief Bioinform在线发表,其算法已包含在QTL.gCIMapping v3.4软件包中。博士生周亚慧为该论文的第一作者,章元明教授为通讯作者。这些研究获得了国家自然科学基金、华中农业大学中央高校基本科研业务费与人才引进启动费以及棉花生物学国家重点实验室开放课题的联合资助。
审核人:章元明
【英文摘要1】
Although genome-wide association studies are widely used in mining genes for quantitative traits, effects to be estimated are confounded and methodologies of detecting interactions are imperfect. To address these issues, first, the mixed model proposed here estimates the genotypic effects for AA, Aa, and aa, while the genotypic polygenic background replaces additive and dominance polygenic backgrounds. Then, the estimated genotypic effects are partitioned into additive and dominance effects using one-way analysis-of-variance model. This strategy was further expanded to cover QTN-by-environment interaction (QEI) and QTN-by-QTN interaction (QQI) using the same mixed model framework. Thus, a three variance components mixed model was integrated with our mrMLM method to establish a new methodological framework that detects all types of loci and estimates their effects, namely 3VmrMLM. In Monte Carlo studies, 3VmrMLM correctly detected all types of loci and almost unbiasedly estimated their effects, with high powers and accuracies and low false positive rate. In the re-analyses of ten traits in 1439 rice hybrids, 269 known genes, 45 known gene-by-environment interactions and 20 known gene-by-gene interactions strongly validated 3VmrMLM. Further analyses of known genes showed more small (67.49%), minor allele frequency (35.52%), and pleiotropic (30.54%) genes, with higher repeatability across datasets (54.36%), and more dominance loci. In addition, heteroscedasticity mixed model in multiple environments and dimension reduction methods in quite a number of environments were developed to detect QEI, and variable selection under polygenic background was proposed in QQI detection. This study provides a new approach to reveal the genetic architecture of quantitative traits.
【英文摘要2】
Detecting small and linked quantitative trait loci (QTLs) and QTL-by-environment interactions (QEIs) for complex traits is a difficult issue in immortalized F2 and F2:3 design, especially in the era of global climate change and environmental plasticity research. Here we proposed a compressed variance component mixed model. In this model, a parametric vector of QTL genotype and environment combination effects replaced QTL effects, environmental effects and their interaction effects, whereas the combination effect polygenic background replaced the QTL and QEI polygenic backgrounds. Thus, the number of variance components in the mixed model was greatly reduced. The model was incorporated into our genome-wide composite interval mapping (GCIM) to propose GCIM-QEI-random and GCIM-QEI-fixed, respectively, under random and fixed models of genetic effects. First, potentially associated QTLs and QEIs were selected from genome-wide scanning. Then, significant QTLs and QEIs were identified using empirical Bayes and likelihood ratio test. Finally, known and candidate genes around these significant loci were mined. The new methods were validated by a series of simulation studies and real data analyses. Compared with ICIM, GCIM-QEI-random had 29.77 ± 18.20% and 24.33 ± 10.15% higher average power, respectively, in 0.5–3.0% QTL and QEI detection, 43.44 ± 9.53% and 51.47 ± 15.70% higher average power, respectively, in linked QTL and QEI detection, and identified 30 more known genes for four rice yield traits, because GCIM-QEI-random identified more small genes/loci, being 2.69 ± 2.37% for additional genes. GCIM-QEI-random was slightly better than GCIM-QEI-fixed. In addition, the new methods may be extended into backcross and genome-wide association studies. This study provides effective methods for detecting small-effect and linked QTLs and QEIs.
论文链接:
3VmrMLM:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2022.02.012
GCIM-QEI:https://academic.oup.com/bib/advance-article/doi/10.1093/bib/bbab596/6527275